One-on-one conversations between managers and employees are a cornerstone of effective management. These meetings promote open communication, build trust and enhance employee engagement. Drawing on best practices and evidence-based strategies, here is a comprehensive guide to conducting successful one-on-one conversations.
Set a Regular Cadence
Why It Matters:
Consistency is key to building trust and maintaining open lines of communication. Regularly scheduled meetings ensure that both parties have a dedicated time to discuss ongoing issues, achievements and future goals
Best Practice:
- Schedule one-on-one’s weekly or bi-weekly, depending on your team’s needs, size and the nature of your work – in person, remote or walk-and-talk.
- Stick to the schedule as much as possible to demonstrate commitment and reliability.
- Use calendar invites to avoid last-minute cancellations.
Create a Comfortable Environment
Why It Matters:
A relaxed atmosphere encourages open dialogue and honest feedback. Employees are more likely to share their thoughts and concerns if they feel at ease
Best Practice:
- Choose a private, quiet space for the meetings to avoid interruptions.
- Avoid meetings at your desk, even though you have your own room. It is your comfort zone, not your employee’s.
- Start with small talk or personal wellbeing check-ins to ease into the conversation. Use the Building a Healthy Workplace: How to Talk to Your Employees About Wellbeing guide, if needed.
- Consider virtual options if remote work is prevalent, ensuring a stable internet connection, space to have a confidential conversation and minimal background noise.
Prepare and Set an Agenda
Why It Matters:
Preparation shows respect for your employee’s time and ensures that the conversation is focused and productive. An agenda provides structure and helps in covering all important topics.
Best Practice:
- Encourage employees to share topics they want to discuss in advance.
- Include both tactical (project updates, task progress) and strategic (career goals, personal development) items.
- Allocate time for both parties to raise spontaneous issues.
Focus on Active Listening
Why It Matters:
Active listening builds trust and shows employees that their opinions and feelings are valued. It also helps in accurately understanding issues and providing appropriate support. See our guide Improving One-on-One Conversations: The Power of Active Listening for more insight.
Best Practice:
- Maintain eye contact and nod to show engagement.
- Avoid interrupting; let the employee complete their thoughts before responding.
- Use paraphrasing and summarising to confirm understanding.
- Ask open-ended questions to encourage deeper discussion.
Provide Constructive Feedback
Why It Matters:
Constructive feedback is essential for growth and improvement. It helps employees understand their strengths and areas for development, fostering continuous learning
Best Practice:
Use the SBI (Situation-Behaviour-Impact) model. The SBI model is a framework for giving clear and effective feedback. It helps focus on specific actions rather than personal attributes, making feedback more objective and constructive.
- Situation: Describe the specific context or event, where the behaviour occurred.
- Behaviour: Focus on the specific actions or behaviours observed, without making judgements.
- Impact: Explain the effect of the behaviour on others, the team or the project.
Example of highlighting positive behaviour with the SBI model:
- Situation: “During our last team meeting, I noticed that you proactively volunteered to lead the new client onboarding project.”
- Behaviour: “You organised a detailed project plan, set clear milestones, and regularly communicated updates to the team and the client.”
- Impact: “Your leadership ensured a smooth onboarding process, which impressed the client and enhanced our team’s reputation. This not only strengthened our relationship with the client, but also boosted team morale and confidence in handling future projects.”
Set Goals and Follow-Up
Why It Matters:
Setting clear goals provides direction and a sense of purpose. Regular follow-up ensures accountability and helps track progress, reinforcing the importance of the agreed-upon actions.
Best Practice:
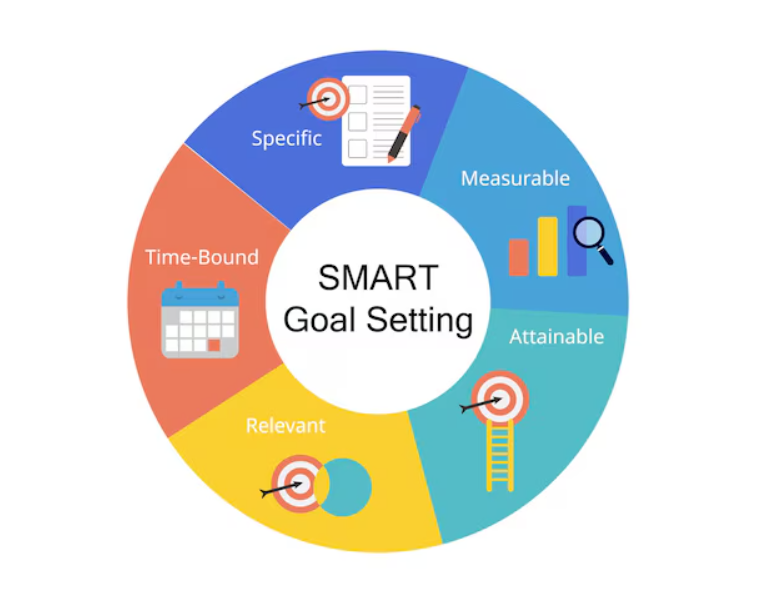
- Collaboratively set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals. See more in our Employee’s Empowerment Toolbox guide.
- Review previous meeting notes to track progress and address any outstanding issues.
- Use a task management tool to keep track of agreed goals.
- Document action items and follow up on them in upcoming meetings.
Show Empathy and Support
Why It Matters:
Empathy strengthens the manager-employee relationship and shows that you care about your employee’s wellbeing. Supportive managers can help employees navigate challenges more effectively
Best Practice:
- Acknowledge personal and professional challenges your employee may be facing.
- Offer support, whether it is resources, flexibility, or simply a listening ear.
- Celebrate achievements and milestones, recognising the employee’s efforts and contributions.
If You Are in Doubt, What to Do?
If You Are in Doubt, What to Do? boxes are designed as a practical, easy-to-use toolkits for managers who want to improve their decision-making and leadership skills.
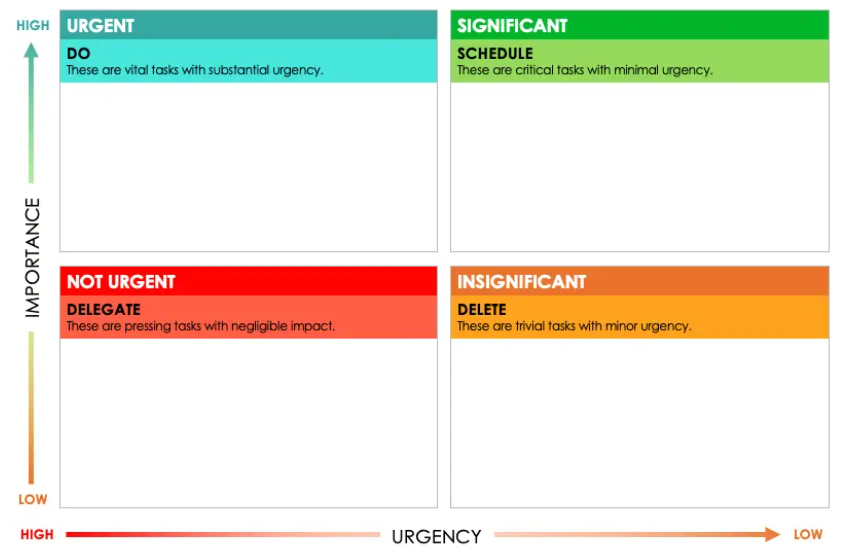
The Eisenhower Matrix for Prioritisation
Purpose: To help prioritise tasks and discussions during one-on-one meetings.
Actions:
- Categorise tasks and topics into four quadrants: Urgent, Not Urgent, Significant and Insignificant.
- Focus on tasks and issues that fall into the “Urgent” quadrant first.
- Use this framework to structure your one-on-one agendas and help employees prioritise their workload.
Benefits: Improves focus on high-priority issues and ensures that important matters are addressed effectively.
The SBI (Situation-Behaviour-Impact) Model for Feedback
Purpose: To provide clear, objective, and actionable feedback.
Actions:
- Situation: Describe the specific context where the behaviour occurred (e.g., “During yesterday’s team presentation…”).
- Behaviour: Focus on the observable actions or behaviours (e.g., “You took the lead in explaining the new project timeline and responded confidently to questions.”).
- Impact: Explain the effect of the behaviour on others, the project, or the team (e.g., “This helped clarify the project’s direction and boosted team confidence.”).
- Use the SBI model during your one-on-one meetings to give balanced, constructive feedback, whether positive or developmental.
Benefits: Provides structured, objective feedback that helps employees understand their actions and the impact, making it easier to replicate or adjust behaviours.
Goal-Setting Techniques and Follow-up
Purpose: To ensure that goals are clear, achievable, and aligned with team objectives.
Actions:
- Collaboratively set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals during one-on-one meetings.
- Regularly review progress on these goals and adjust as necessary.
- Document goals and track progress using a simple tracking method or tool.
Benefits: Ensures that goals are clear and progress is measurable, enhancing accountability.
In Conclusion
Having regular one-on-one meetings with a clear agenda, where your focus lies on active listening, providing constructive feedback, setting goals and demonstrating empathy and support is the best practice to nurture open communication, trust and employee growth. By using these practices consistently, you will strengthen relationships with your team members and drive both individual and team success.
References
- Buckingham, M., & Goodall, A. (2016). How to Make Your One-on-Ones with Employees More Productive. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2016/08/how-to-make-your-one-on-ones-with-employees-more-productive (01.08.2024)
- Center for Creative Leadership. (n.d.). How to Give Constructive Feedback. Center for Creative Leadership. Retrieved from https://www.ccl.org/articles/leading-effectively-articles/giving-feedback-what-every-leader-needs-to-know/ (01.08.2024)
- Forbes Human Resources Council. (2018). The Importance Of Active Listening In The Workplace. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbeshumanresourcescouncil/2018/08/31/the-importance-of-active-listening-in-the-workplace/ (01.08.2024)
- Gallup. (n.d.). The Power of Goal Setting: A Leader’s Guide to Aligning Employee Purpose and Performance. Gallup. Retrieved from https://www.gallup.com/workplace/247577/power-goal-setting-leader-guide-aligning-employee-purpose-performance.aspx (02.08.2024)
- Keller, S., & Meaney, M. (2018). The Boss Factor: Making the World a Better Place through Workplace Relationships. McKinsey & Company. Retrieved from https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/organization/our-insights/the-boss-factor-making-the-world-a-better-place-through-workplace-relationships (02.08.2024)
- MindTools. (n.d.). Running Effective Meetings. MindTools. Retrieved from https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newLDR_76.htm (02.08.2024)
- Society for Human Resource Management. (n.d.). How to Conduct a Performance Review. SHRM. Retrieved from https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/how-to-guides/pages/conducting-a-performance-review.aspx (02.08.2024)
- https://engagedly.com/blog/importance-of-sbi-when-giving-feedback-in-workplace/ (07.08.2024)